The Midwest Glacial Lakes Partnership (MGLP) is awarding $305,584 through its 2025 Lake Conservation Grant to five projects across the Upper Midwest. Together, these projects will benefit glacial lakes and their fish habitats, fish populations, and fisheries for years to come.
Funds for the Lake Conservation Grant are provided by the US Fish and Wildlife Service and will be matched by over $700,000 in contributions from project partners, for a total conservation investment of over $1,000,000.
The five projects funded by the 2025 Lake Conservation Grant are listed below.
- Acre-for-acre restoration of lake hydrology and Northern Pike spawning habitat for Cedar Lake (Michigan), Cedar Lake Improvement Board – $84,310
- Advancing a statewide Lake Steward Program to promote natural shorelines and fish habitat, Minnesota Lakes and Rivers- $58,250
- Ottawa County (Michigan) natural shoreline restoration project, Ottawa Conservation District – $68,385
- Walleye habitat engagement in Wisconsin, Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources – $12,741
- Midwest Glacial Lakes Partnership operations, Michigan Department of Natural Resources – $81,898
The Lake Conservation Grant is operated annually by the MGLP as a member of the National Fish Habitat Partnership. Curious to learn more about past MGLP projects? You can find a map of past projects on the National Fish Habitat Partnership’s Project and Accomplishments Dashboard.
Those interested in future grant applications can find more information on the Lake Conservation Grant page of the MGLP website and can sign up for this MGLP Newsletter to receive notifications if not already subscribed. Read more below about the projects that received funding this year.
Acre-for-acre restoration of lake hydrology and Northern Pike spawning habitat for Cedar Lake – $84,310
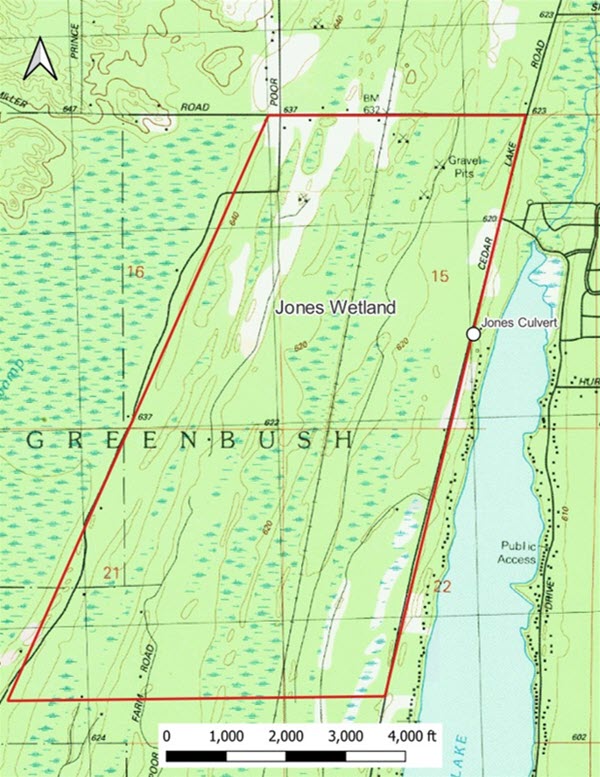
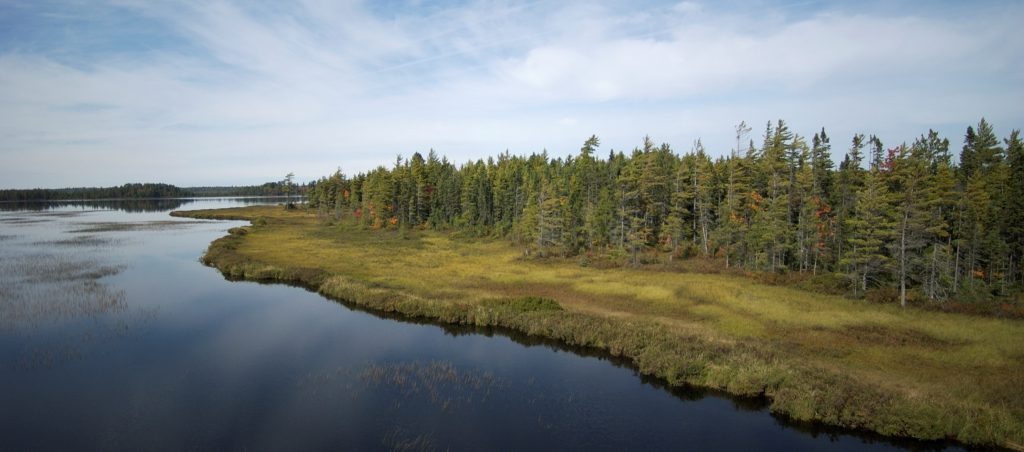
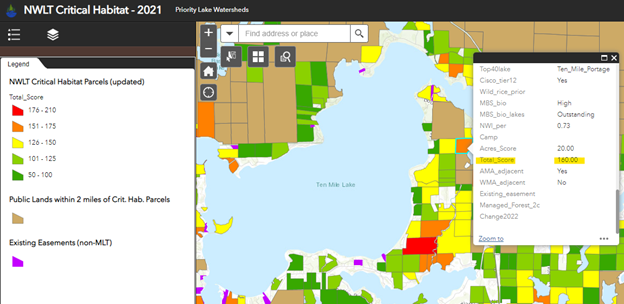
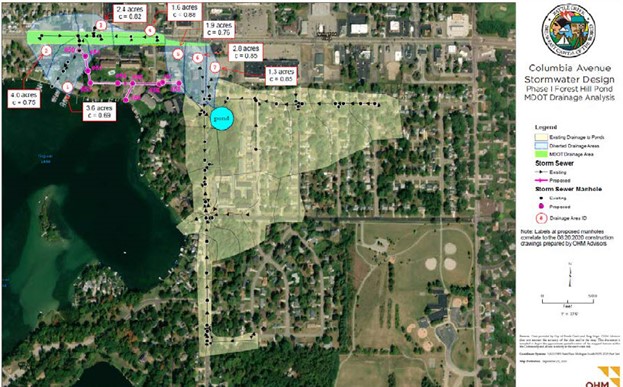
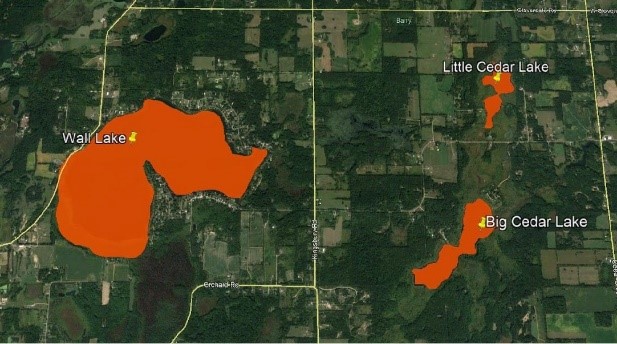
Cedar Lake is a 1,050-acre glacial lake on the northeastern side of Michigan’s Lower Peninsula. Only two small streams deliver surface water to the lake from its watershed: Sherman Creek to the South and Jones Ditch to the North. These connections with the watershed, which is mostly wetlands, were disrupted in the 1970’s by roadway drainage infrastructure. Since good record-keeping began in 2004, documented lake levels have dropped as much as 28 inches in the Summer due to these historical modifications. Comprehensive lake level and watershed hydrology monitoring has shown that these hydrological disruptions are particularly problematic during dry summers when surface flows are limited. Efforts to reconnect Sherman Creek have already been successful at partially restoring the lake’s hydrology. This project will restore the Jones Ditch channel and reconnect Cedar Lake to spawning habitat in the 1,019-acre Jones Wetland that the ditch drains. Additionally, the project will develop engineering designs to replace two culverts that disrupt stream flow into the lake, ultimately restoring the lake’s natural lake levels.
Advancing a statewide Lake Steward Program to promote natural shorelines and fish habitat, Minnesota Lakes and Rivers – $58,250
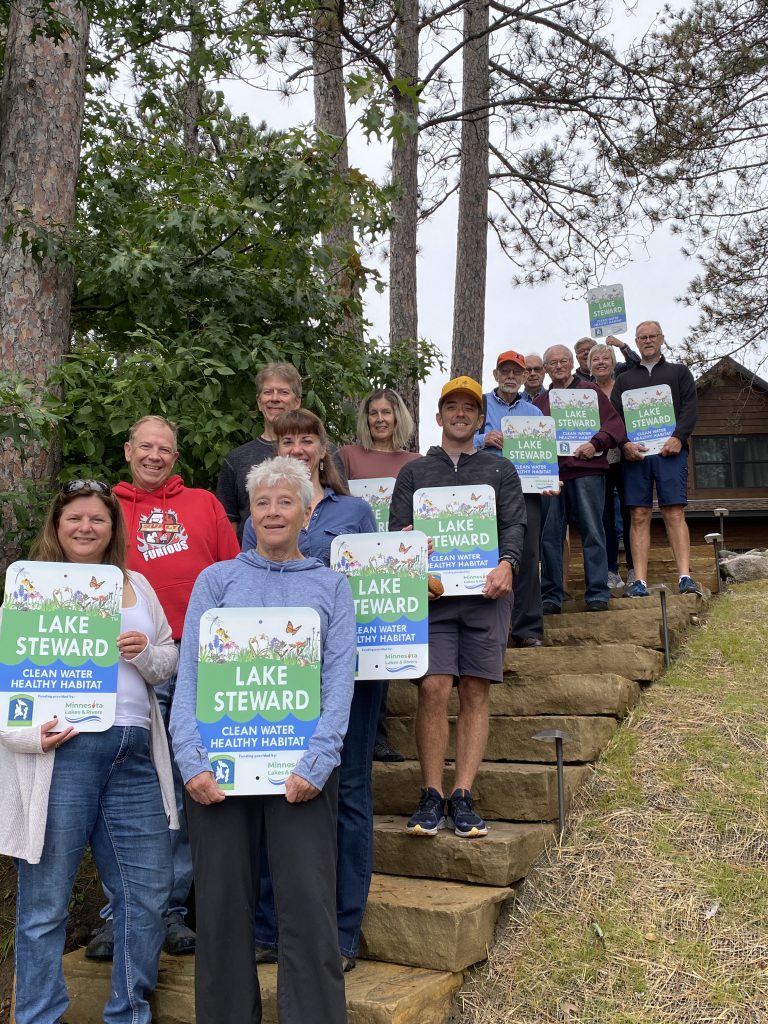

Minnesota Lakes and Rivers (MLR) believes that lakeshore property owners need support and guidance on good shoreline stewardship, and community leadership can shift social norms toward protecting and restoring natural shorelines. This project will train lake association members to evaluate shoreland properties and provide support to property owners improving their lake stewardship for water quality and fish habitat. Second, MLR will work with lake associations and the Minnesota Natural Shoreline Partnership across the state to raise awareness on the importance of natural shorelines through training and outreach for lakeshore owners, landscapers, and consultants. Third, MLR will partner with the Oneida County (WI) Lakes and Rivers Association to advance both organizations’ regional Lake Steward programs.
Ottawa County natural shoreline restoration project, Ottawa Conservation District – $68,385
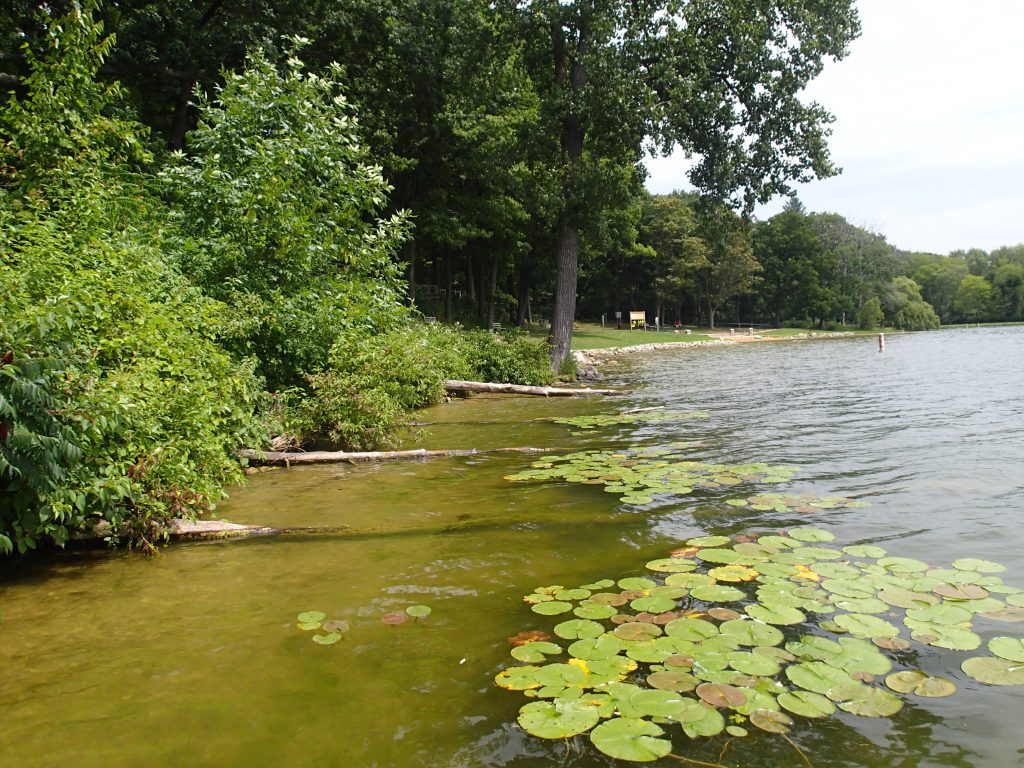

Ottawa County (Michigan) contains several inland lakes with dense human residential development. Construction, land use change, and recreational activities have caused shoreline erosion, which has been addressed historically through hard armoring and the installation of seawalls. Unfortunately, this leads to negative ecological impacts through shoreline and nearshore habitat loss. Ottawa Conservation District staff will provide information and technical assistance to lakefront landowners through mailers, social media, public presentations, events, and workshops. This information will focus on native plantings as an alternative to turf grass, bioengineering as an alternative to seawalls and “hard armoring” techniques, and promotion of other types of shoreline habitat protection, restoration, and improvement. Ottawa Conservation District will then help landowners develop projects to address these needs. Finally, this effort will provide cost share funds to help reduce out-of-pocket costs for landowners to implement natural shoreline designs on their property.
Walleye Habitat engagement in Wisconsin, Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources – $12,741
This project is a two-pronged approach for Walleye habitat protection and rehabilitation efforts to engage both a broad group of lake stakeholders in Wisconsin as well as target specific stakeholders that are shoreline property owners. Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (WI DNR) will create a short, engaging video showing how to protect Walleye habitat for anglers, lake associations, and conservation groups. This video will be accessible and easy to share in a digital format, so that it can reach a wide audience. WI DNR will take a complimentary and more targeted approach sending materials including the video and site-specific Walleye habitat information directly to shoreline owners along key Walleye spawning shorelines that will be identified by biologists on a set of high priority lakes. This effort will educate and engage private shoreline owners who make critical shoreline habitat decisions that can harm or benefit Walleye. Building these relationships with landowners is expected to accelerate shoreline protection and rehabilitation efforts.
Midwest Glacial Lakes Partnership operations, Michigan Department of Natural Resources – $81,898
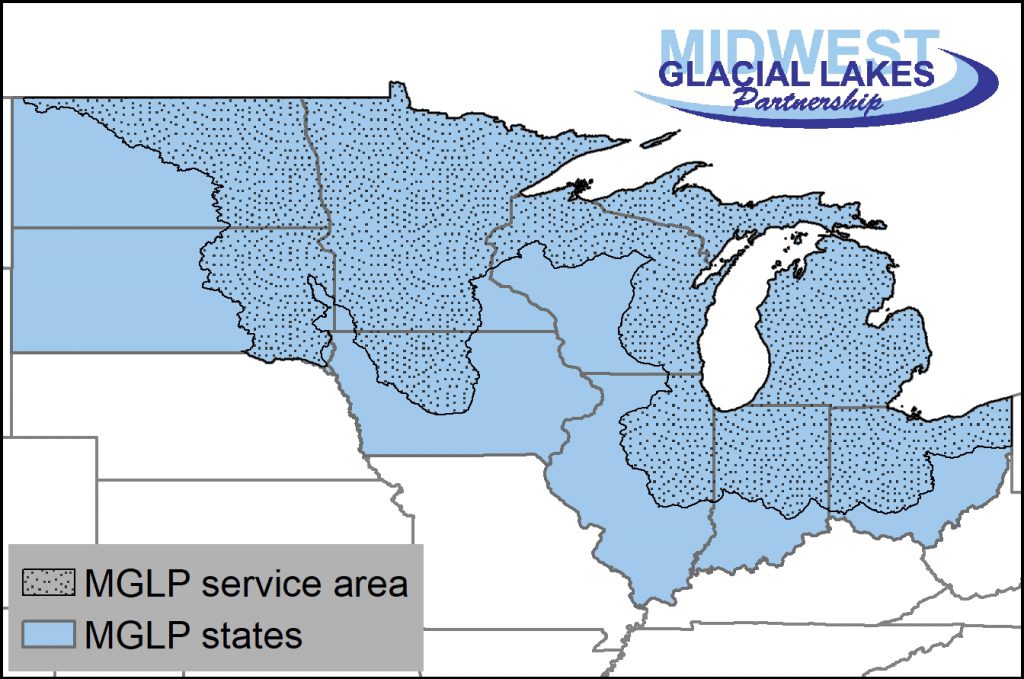
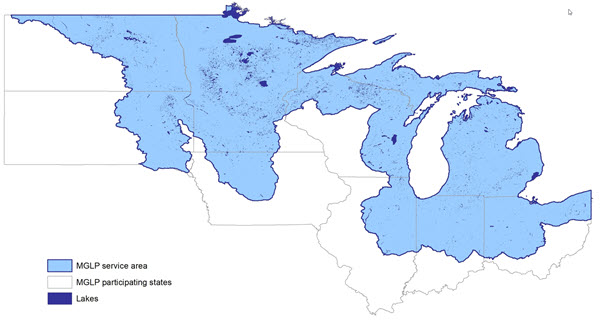
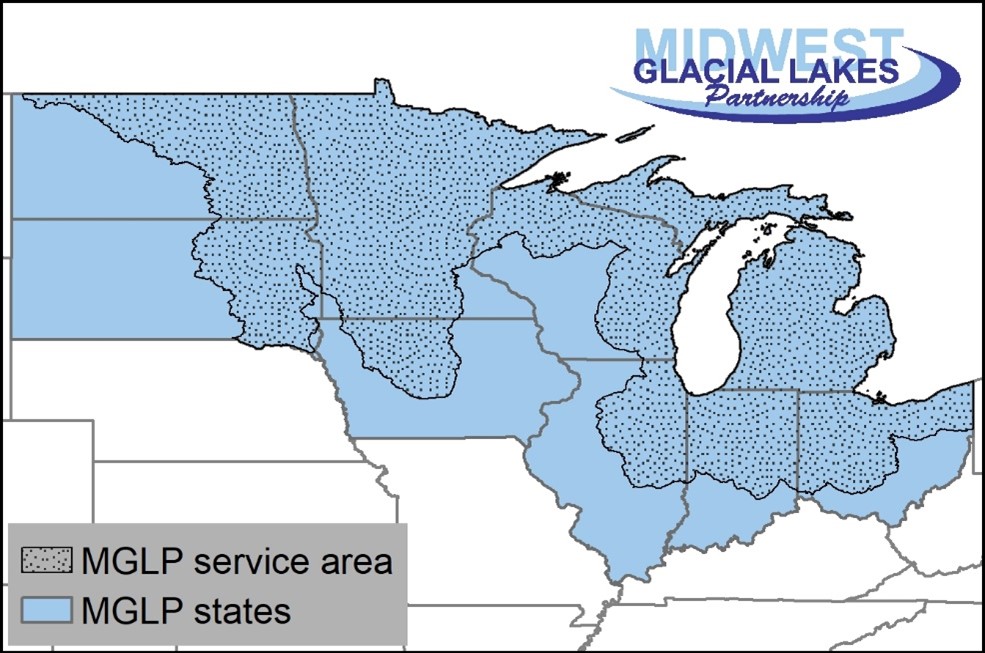
The Midwest Glacial Lakes Partnership works to protect, rehabilitate, and enhance sustainable fish habitats in glacial lakes of the Midwest for the use and enjoyment of current and future generations. Partnership staffing is limited to the coordinator, and funding for that position is required to coordinate the partnership’s three committees, implement tasks delegated by the committees to the coordinator, maintain partnership operations in support of the partnership’s mission, goals, and objectives, and participate in the National Fish Habitat Partnership. This project supports the coordinator and provides an operations budget for partnership activities including printing copies of the partnership’s Shoreline Living publication, revising the website, and others.